Modules
Modules are pieces of code that other people have written to fulfill common tasks, such as generating random numbers, performing mathematical operations, etc.
The basic way to use a module is to add import module_name at the top of your code, and then using module_name.var to access functions and values with the name var in the module. For example, the following example uses the random module to generate random numbers
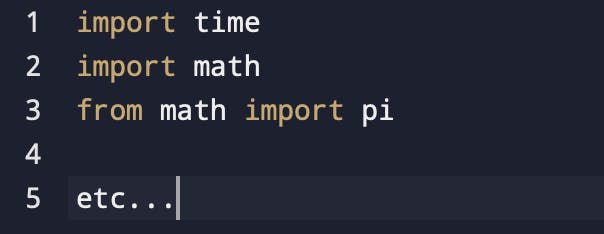
They look like this:
⚠ Importing a module that doesnot exist gives errors.
How To Install The Modules?? :-
Many third-party Python modules are stored on the Python Package Index (PyPI). The best way to install these is using a program called pip. This comes installed by default with modern distributions of Python. If you don't have it, it is easy to install online. Once you have it, installing libraries from PyPI is easy. Look up the name of the library you want to install, go to the command line (for Windows it will be the Command Prompt), and enter pip install library_name. Once you've done this, import the library and use it in your code.
Using pip is the standard way of installing libraries on most operating systems, but some libraries have prebuilt binaries for Windows. These are normal executable files that let you install libraries with a GUI the same way you would install other programs.